Learning-AI
Transformer: Attention Is All You Need
June 2020
tl;dr: Transformer architecture to get the SOTA.
Overall impression
Transformer introduced attention mechanism and successfully applied to NLP.
This is followed up by other SOTA methods in NLP such as BERT, but the idea of using attention module as the basic building block of a neural network is profound.
Attention, as opposed to memory, has constant length between any two positions. Sometimes attention is said to have “perfect memory”.
Key ideas
- Three different types of attention
- Self-attention in encoder
- Self-attention in decoder
- Cross-attention between encoder and decoder
- Encoder: self-attention + FFN (feed forward network). Dependencies in diff words of input in self-attention layer, but FFN is independent.
- Decoder: autoregressive. Each step generates one output.
- Attention:
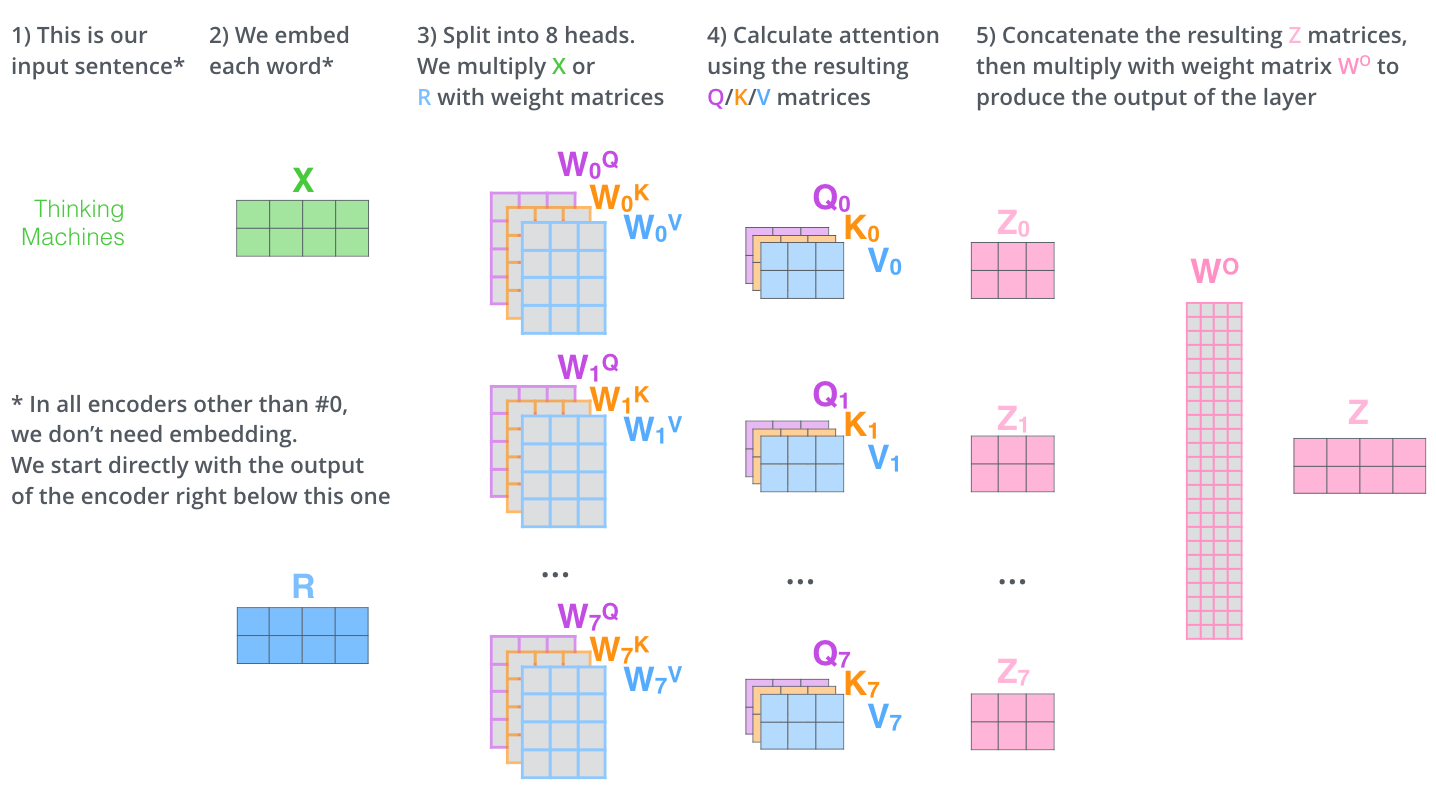
- Self-attention: Q, K, V. K and V is a form of dictionary and a form of memory. Q and K could be the same thing, but not necessarily. The encoder is essentially building a dictionary. \(\text{Attention}(Q, K, V) = \text{softmax} (\frac{QK^T}{\sqrt{d_k}}) V\)
- (scaled) Dot-product attention.
- Multi-head self-attention: split into parallel heads and embed into diff representation space
- Masked self-attention in decoder: prevent looking forward
- Encoder-decoder attention: Q is from decoder, but K, V from encoder
- Self attention sees its input as a set, not a sequence. If we permute the input sequence, the output sequence will be exactly the same, except permuted also (i.e. self-attention is permutation equivariant).
- Therefore we need positional embedding
Technical details
- Positional embedding (PE): there is no notion of word order (1st word, 2nd word, ..) in the proposed architecture, and thus model has no idea how the words are ordered. However when the order matters (A chases B vs B chases A), we need to input additional order information to the architecture. The encoding is not part of the model but rather enhances the input. In this sense it is a bit like CoordConv.
- It is a generalization of binary encoding.
- Linear encoding [0, 1]: time-step delta does not have consistent meaning for seq of diff length.
- Linear integer encoding: unbounded
- Desired characteristics:
- Bounded
- Deterministic
- Unique for position i
- Distance between any two step should be consistent for seq of diff len.
- There is a fixed linear transformation from two embeddings with a fixed distance apart. “We chose this function because we hypothesized it would allow the model to easily learn to attend by relative positions, since for any fixed offset k, PEpos+k can be represented as a linear function of PEpos.”
- The distance between positions (via dot product) decays symmetrically and smoothly.
- Positional embedding is added but not concatenated. Basically PE only takes small number of dimensions and large portion of the high dim space is occupied by WE (“Near orthogonality in high dim space” property).
- Softmax: The term “soft” derives from the fact that the softmax function is continuous and differentiable. The arg max function, with its result represented as a one-hot vector, is not continuous or differentiable. The softmax function thus provides a “softened” version of the arg max. (Source)
Notes
- Simplest self attention
# assume we have some tensor x with size (b, t, k)
x = ...
raw_weights = torch.bmm(x, x.transpose(1, 2)) # (b, t, t)
weights = F.softmax(raw_weights, dim=2) # (b, t, t)
y = torch.bmm(weights, x) # (b, t, k)
- Illustrated Transformer
- Yannic Kilcher’s video
- About positional encoding
- It is a continuous way to do binary encoding. It is easier for the network to look at different channels and figure out how far away two samples are. source1 and source2
- Review on 知乎Zhihu
- Review blog about positional encoding
- Reddit post
- ipython notebook from Google Research explaining PE

- RNNs:
- long path for information flow between encoding and decoding a word
- machine translation cannot do 1:1 mapping.
- attention helps to pinpoint important bits even across long ranges. It gives decoder a way to directly attend to all input hidden states rather than to go through them one by one.
- In RNN, the entire seq-to-seq is one training sample. –> In transformers, every step is one training sample.